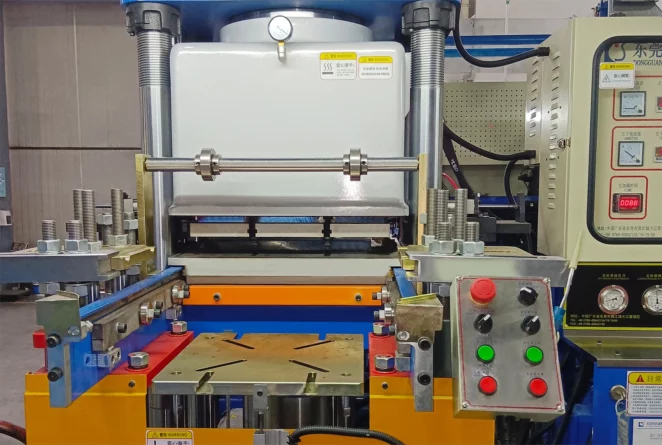
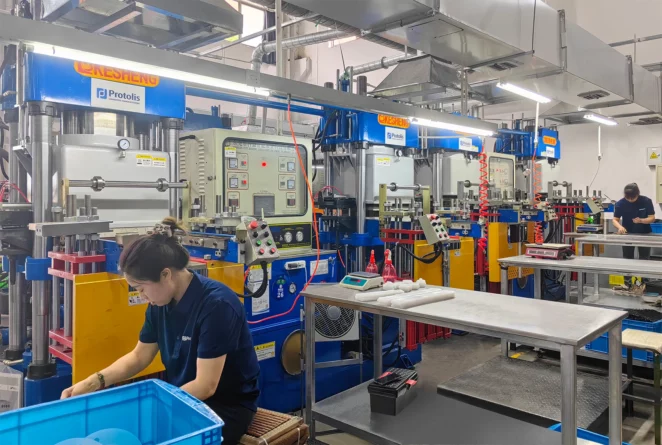
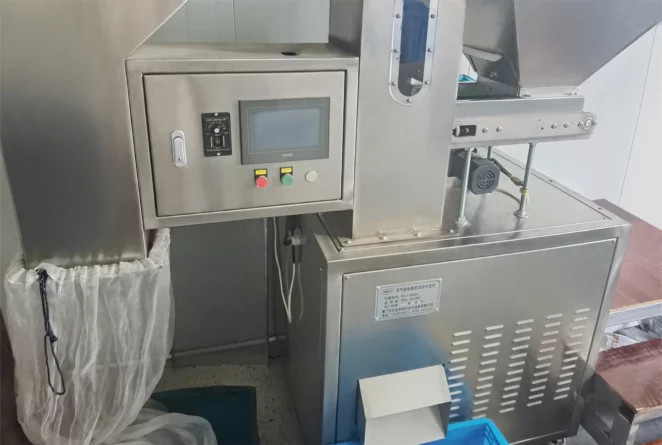
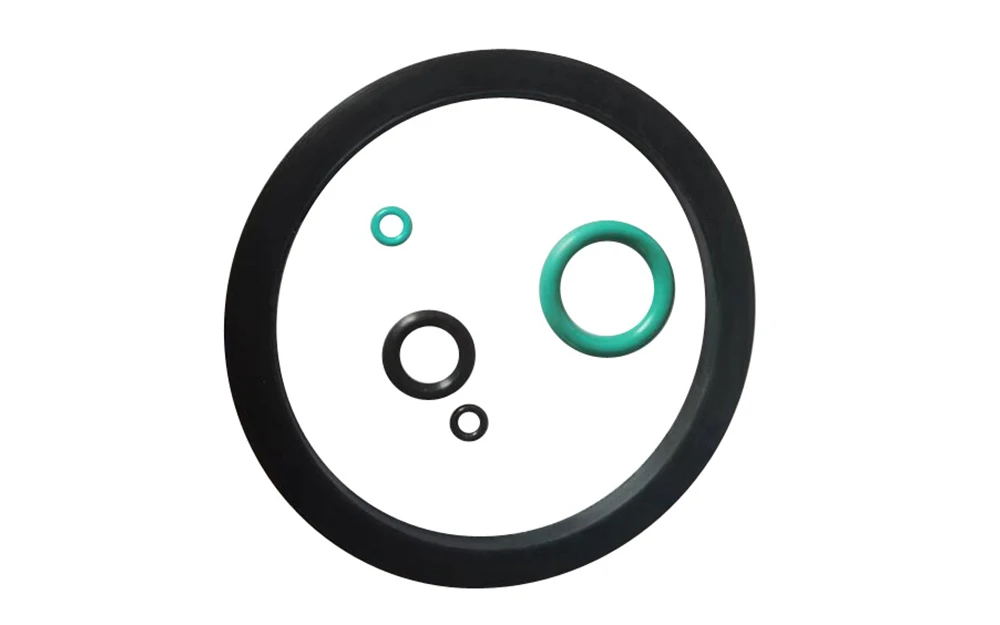
Compression molding service
At Protolis, we combine advanced rubber and silicone compression molding capabilities with global service to support your project from early prototypes to low- and high-volume production. We deliver consistent, high-quality molded parts worldwide with fast lead times and cost-effective tooling.
- 1 to 1000+ parts
- Wide variety of materials available (silicon, plastic, rubber EPDM, PU)
- Versatile manufacturing capabilities
- Low compression tooling cost
- Ready in 10-20 days
What is compression molding?
Compression molding is a manufacturing process used to produce high-quality rubber, silicone, and thermoset parts for prototypes and low- or high-volume production. A pre-measured preform is placed in a heated mold and compressed until it fills the cavity and cures into the final geometry.
Engineers choose compression molding for its low tooling cost, fast lead times, and ability to create durable, functional parts with production-grade materials. It is an ideal solution for rubber and silicone prototyping, small-series molding, and applications requiring strong, heat- and chemical-resistant components without the expense of injection molds.
What is compression molding?
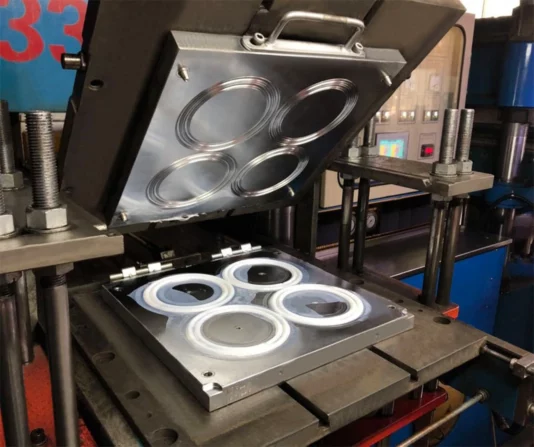

Additional compression molding capabilities
Our compression molding capabilities offer a diverse range of options to produce compressed parts with varying lengths, thicknesses, shores and complexities.

Rapid tooling
Thanks to the optimization of our prototype molds, we offer our clients reduced production times and minimized geometric constraints.

Overmolding
Our molding capabilities allow the incorporation of metal inserts or other components, resulting in integrated parts with the combined benefits

Assembly
Our service enables seamless integration of your compressed parts with other, facilitating efficient assembly of your final product.
Compression molding capabilities
At Protolis, we bring extensive experience and proven expertise in compression molding through strong partnerships with trusted manufacturers. Our engineering-focused team ensures rigorous project management, emphasizing quality, precision, and timely delivery. We conduct thorough post-production quality checks and manage in-house post-processing operations such as assembly to maintain full control over performance and consistency. With a streamlined workflow and deep industry knowledge, we offer quick turnaround times without compromising on quality.
Your compression molding project in 6 steps
Get your plastic low shore prototypes or production parts in no time. A flexible organization providing a personalized response to your need without any setback.
Your quote
Upload files and specifications
DFM
Design optimizations
Tooling
Sampling and adjustments
Production
Close follow-up
Quality control
Dimensional report, pictures, and videos
Delivery
Packing, door-to-door tracking
Applications
Compression molded parts are used across a wide range of industries. In automotive and industrial sectors, this process is ideal for producing strong, durable components such as gaskets, seals and hoses. For custom and niche manufacturing, its suitability for low to medium volumes makes it a practical and economical choice. In rubber applications, compression molding excels when elastomeric properties like flexibility and resilience are needed. It’s also well-suited for the electrical and electronics industries, where heat resistance and insulation are critical.
Compression molding materials
We offer a wide range of materials such as elastomer, silicone rubber, and thermoset materials for customizing your prototype and low-volume production parts. Below is a non-exhaustive list of commonly used materials for compression molding.
Compression molding finishes
There are several finishing options available. Explore a selection of finishing choices that enhance the appearance, functionality, and durability of prototyping compression parts.

The pigmentation process makes it possible to produce pieces naturally colored in the mass of certain plastics. It is possible to choose the desired RAL or Pantone, with color pigments mixed with the material. This is applicable for rigid or flexible parts.

Whether by applying a surface treatment or by pigmentation, matching the colors of your prototypes and parts is important for meeting your specifications and the visual quality of the final product.

We offer various methods to print or engrave your logo, texts, and symbols to give a finished appearance to your pieces.
General compression characteristics
Why Work With Protolis for Compression Molding?
- Cost-efficient small-series production with low-cost tooling
- Fast lead times — tooling in 10–20 days, production in 7–15 days
- From prototype to high-volume production
- Strong expertise in rubber and silicone materials
- ISO 9001–based quality control for consistent
- Engineering support and DFM review
Why Work With Protolis for Compression Molding?
Compression molding FAQs
What are the advantages and disadvantages of compression molding?
Compression molding offers simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it accessible even for applications with undercuts. It excels in molding thick and soft materials, such as silicone and high-temperature variants, setting it apart from other methods. However, it has limitations, including a relatively slower production speed, making it unsuitable for very high volumes. Complex designs may also pose challenges due to the method’s simplicity and constraints in achieving intricate shapes.
How compression molding works?
Compression molding is a relatively straightforward technique that entails applying pressure to a pliable material charge by sandwiching it between two halves of a heated mold. Once the material cools or cures, it takes on the shape of the mold, resulting in a molded part. This method commonly employs substantial tonnage presses, ranging from 150 to 2,500 tons, and heated dies.
Is compression molding suitable for low volume production?
The advantages and disadvantages align with the requirements for low-volume production. It fits perfectly with what we need for low-volume manufacturing.
More resources

Compression Molding guide

Overview of Medical Device Regulations [Guide]